What occurs to the physique when an individual will get heatstroke? How can we defend ourselves in a warming planet? To reply these burning questions, Arizona researchers deployed a robotic that may breathe, vibrate and sweat.
The southwestern state capital of Phoenix is at the moment enduring its longest warmth wave in historical past: On Friday, temperatures topped 110 levels Fahrenheit (43 levels Celsius) for the 22nd day in a row, an ominous signal of what is to come back. Change in ambiance.
For people, such warmth represents a doubtlessly deadly risk, which remains to be not absolutely understood. However for ANDI — a form of humanoid robotic at Arizona State College — it is a phenomenal day.
“It is the world’s first outside thermal model that we are able to recurrently take outdoors and … measure how a lot warmth it is getting from the atmosphere,” mechanical engineering professor Konrad Rykazewski advised AFP.
ANDI is a really reasonable approach to experimentally measure how people reply to excessive climates with out placing folks in danger, Rykaczewski says.
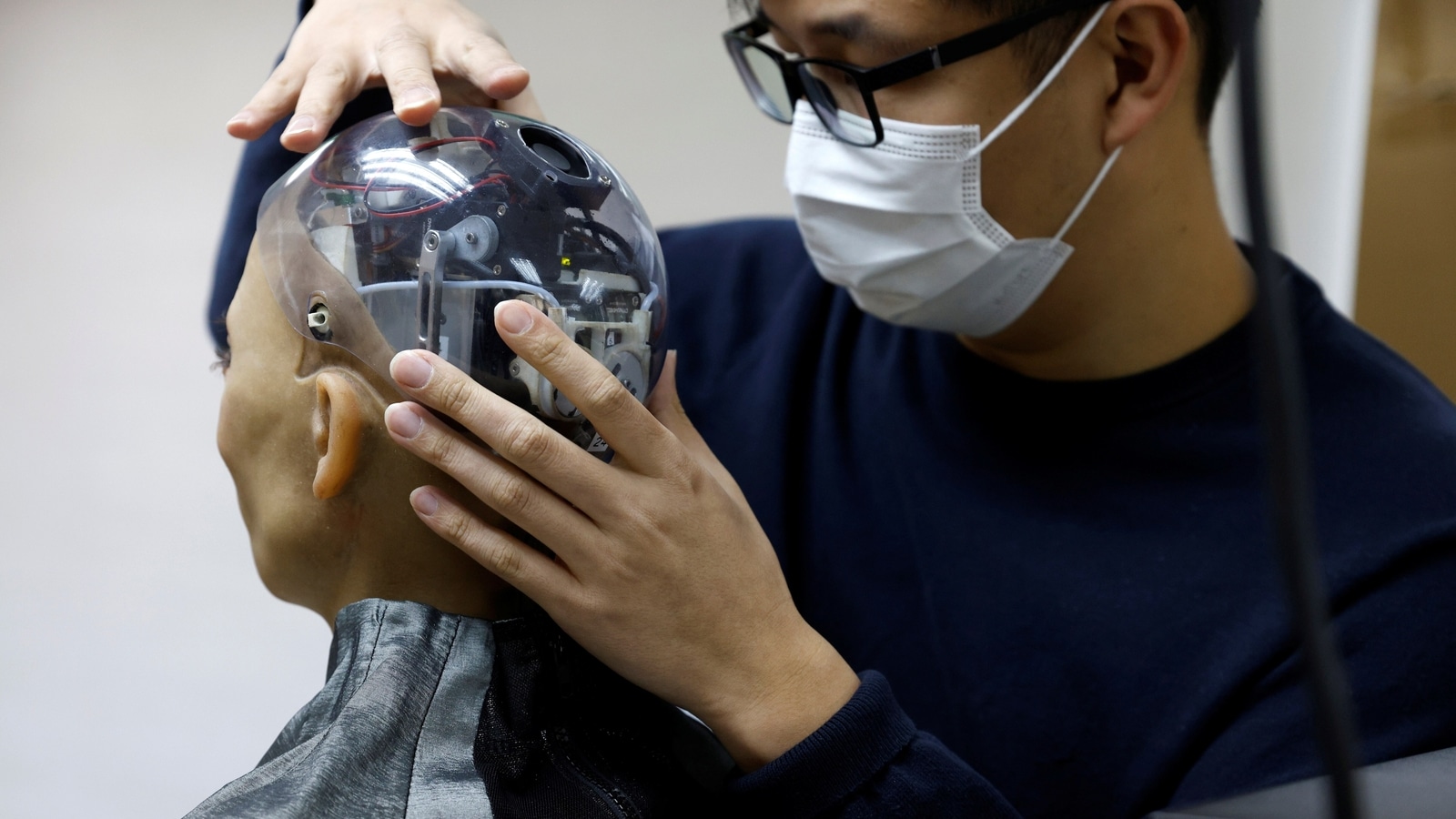
At first look, ANDI — which stands for Superior Newton Dynamic Instrument — appears like a easy crash-test dummy.
However its epoxy/carbon fiber pores and skin hides a wealth of expertise, comparable to a community of linked sensors that assess physique warmth.
The ANDI additionally has an inside cooling system and holes that enable it to breathe and sweat. There are 35 unbiased thermal zones and, like people, Robotic — which value greater than half 1,000,000 {dollars} to make — will get extra sweat off his again.
Till now, solely a dozen or so mannequins of this sort existed, and none of them may enterprise outdoors.
They have been primarily utilized by sports activities tools producers to check their technical clothes in thermal chambers.
Hyperthermia, a 21st century situation
Researchers hope the robotic will present a greater understanding of hyperthermia — that’s, when the physique overheats, a situation that threatens a rising proportion of the world’s inhabitants. world warming.
For apparent moral causes, “nobody measures the rise in core temperature when somebody has heatstroke,” Rykazewski says. However the results of warmth on the human physique are nonetheless not absolutely understood. ANDI affords researchers a chance to know
Together with MARTy (Imply Radiant Temperature), a cell climate station that measures warmth mirrored by buildings round it, the robotic is taking its first steps outdoors of Phoenix—an excellent laboratory during which to arrange for tomorrow’s local weather.
“How do we modify what we put on? How do we modify our habits patterns, and alter them to temperatures of this order of magnitude?” Rykaczewski says.
Andy can also be infinitely reprogrammable. Jennifer Vanos, a climatologist concerned within the undertaking, explains that the analysis group “can create digital twins of mannequins to have a look at completely different elements of the inhabitants.”
For instance, the older you get, the much less you sweat. Younger folks will want completely different safety from athletes or folks unwell. With ANDI, scientists can simulate thermoregulatory mechanisms distinctive to every particular person.
Phoenix, a check lab for the long run
They’ll additionally check the robotic in numerous conditions. For instance, Phoenix is dry — what in regards to the humid warmth? How does the human physique deal with scorching winds?
Their analysis shall be helpful in designing heat-resistant clothes, rethinking city planning and defending essentially the most weak.
In Phoenix, which opens dozens of cooling facilities for the homeless each summer time, their findings may information the actions of social employees.
“How lengthy does an individual have to remain in a cooling heart to chill down sufficient for his or her core temperature to drop again right down to a stage that is secure? We will reply that query with Andi,” Vanos says.
The group additionally goals of growing low-cost sensors to regulate working hours on constructing websites to match the warmth and employee well being truly skilled on web site — not primarily based on regular. the climate circumstances
That “may very well be a step towards higher security than these empty suggestions per metropolis, per state, per nation,” Rykaczewski says.
Such particular, tailor-made options can have world results, reshaping total cities.
“If the way forward for Paris appears just like the Phoenix now, we are able to study lots about how we design buildings,” Rykaczewski says.